What is Child (Pediatric) Radiology?
It is the department that makes the radiological evaluation of individuals between the ages of 0-16. Since children continue to grow and develop, there is a need for evaluation in centers that know their developmental stages and can plan different doses than adults, both in evaluation and in examinations working with radiation such as direct radiography and computed tomography.
Why Pediatric Radiology?

‘CHILDREN ARE NOT LITTLE ADULTS!’ This is even more important, especially when it comes to health. Examination by people who have detailed knowledge and experience about the child’s unique diseases and diseases that occur in all age groups but have a different prognosis in children provide trust and support to both the clinician and the family during the diagnosis and treatment process. In our center, your children are evaluated by a specialist radiologist who has received minor specialization training in Cerrahpaşa Pediatric Radiology for 2 years and has scientific studies on this subject.
Some radiological examinations work with radiation, but arrangements can be made regarding the dose value to be taken according to the patient. Especially in pediatric patients, it is important to adjust the dose of the investigation according to the child. This is meticulously implemented in our center.
Which Radiological Examinations Are Performed in Children?
Ultrasound, color ultrasound, computed tomography, dental film, fluoroscopic examinations and X-ray film are taken and evaluated for children.
Ultrasound and color ultrasound are radiological examinations that can be safely applied to children that do not contain radiation.
Thyroid, lymph nodes, breast tissue, inguinal, subcutaneous lesions, muscle and tendon structures, joints, all internal organs (liver, gall bladder, pancreas, spleen, kidneys, adrenal glands, intestines, urinary tract, urinary bladder, ovary) with ultrasound , uterus, testis, prostate) can be evaluated.
Since the fontanelle is open in the first 3 months, the brain and intracranial structures can be evaluated with cranial ultrasound.
Screening is performed for developmental dysplasia of the hip (hip dislocation), which is the most common musculoskeletal disease in the neonatal period in our country. This scan is done by Ultrasound between 1-6 months and full treatment is possible with early diagnosis.
The dimple seen in the waist, called sacral dimple, in the neonatal period is sometimes an indicator of problems related to the spinal cord and spinal canal. In such patients, ultrasound evaluation is performed in the early period.
With Doppler Ultrasound (Color Ultrasound), all vascular structures, vascularization of organs, vascular occlusions, and if there is a lesion, lesion blood supply are shown. In addition, it is very important to evaluate the vascular structures of the relevant organ with color ultrasound in the examination of ovarian or testicular torsion, which is seen in childhood and requires emergency treatment.
Computed Tomography is an examination method that provides detailed information, but works with radiation, in which 3-dimensional, cross-sectional images are obtained. For this reason, it is very important to adjust the dose in pediatric patients and to shoot by protecting the radiation sensitive areas. Since it is a short examination, children who need to stand still can usually tolerate it or the examination can be done while they are sleeping. Detailed evaluation of all internal organs, brain, bone structures and soft tissue is possible with CT. In cases where medicated (contrast) CT is required, the necessary premedication is planned for those with a history of allergy, and the examination is performed by intravenous contrast agent (drug) according to your child’s weight. Contrast material is necessary for determining the vascular structures and the character of the lesions, if any.
In cases such as X-ray and Dental X-ray, growth retardation, short stature, bone age is evaluated with left wrist X-ray.
Chest X-ray, sinus X-ray, head X-ray, standing direct abdominal X-ray, X-rays of bone structures, intravenous pyelography and many other radiographs are taken in our center by adjusting the dose appropriate for the child. In addition, necessary protection is made so that the areas outside the examination area are not exposed to radiation.
Fluoroscopic examinations; Esophagus (esophagus) passage X-ray, small bowel X-ray, voiding (voiding) cystoureterography, contrast-enhanced colon X-ray fistulography are performed. In patients with congenital esophageal strictures or after ingestion of corrosive substances, fluoroscopic examinations are performed to evaluate diaphragm movements in small intestine diseases (inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease..), large intestine disease (Hirschsprung disease.. etc.).
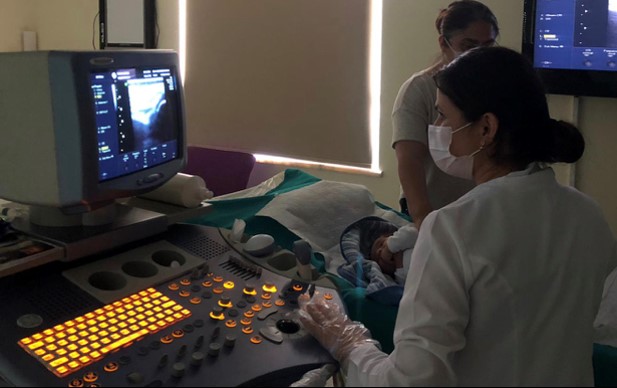
***While your child watches the cartoon on the LCD screen in each ultrasound room, your doctor completes the examination. On the same day, your procedure is completed in a hygienic environment without waiting in line, and you can get your report and go home right after.

